These days the Arab region is witnessing a severe and unusual heat wave, amid warnings that the temperatures continue to rise to record levels in some areas.
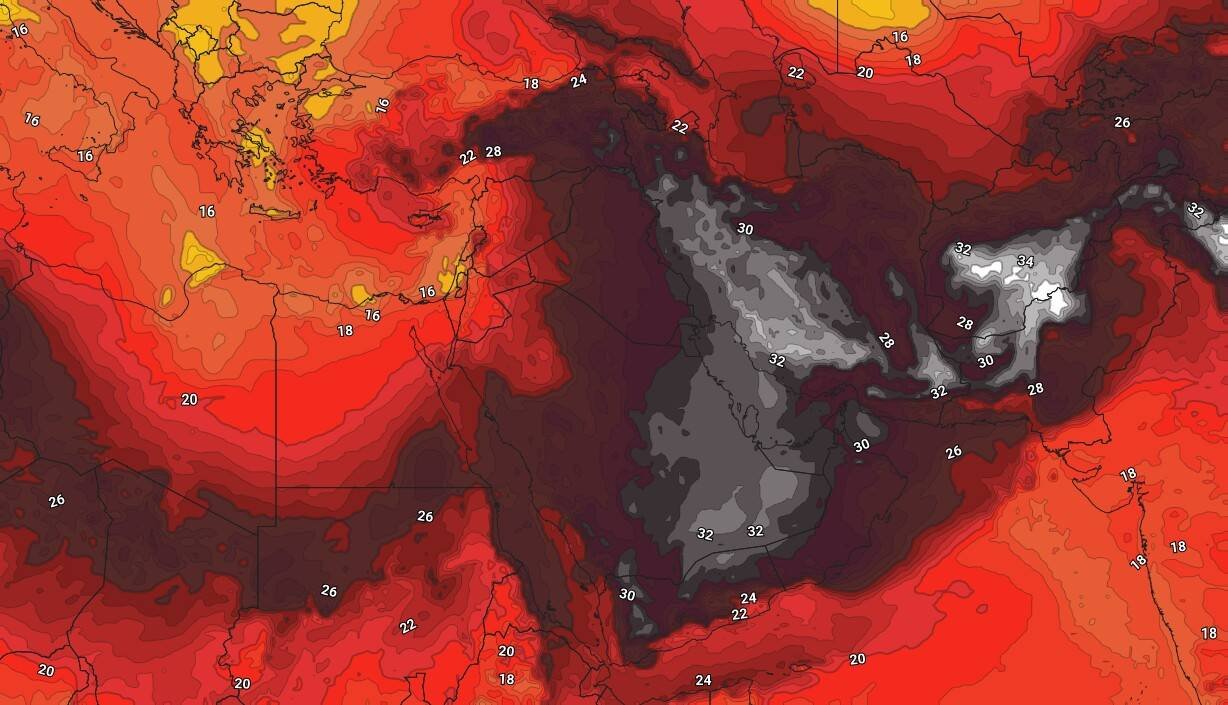
The analyzes of the “Arab Weather” website indicate the expansion of the region affected in the coming days, in the coming days, known as the “thermal dome”, which is a highly hot air mass stationed in the upper atmosphere, and is especially focused over Iraq, Kuwait and eastern Saudi Arabia. It is expected that the concentration of this flame bloc over Iraq is expected to lead to a significant rise in temperatures, which may exceed 50 degrees Celsius in the capital, Baghdad, which places it among the world’s most hot cities at the beginning of the week.
This height is also attributed to the growing effect of the semi -tropical atmosphere, which enhances the intensity of the thermal dome, to reach its climax in Iraq, Kuwait and eastern Saudi Arabia, and it is currently among the most heat areas on the surface of the earth. The effects of this mass also extend to the Levant, where a more hot atmosphere prevails than usual, while Egypt recorded temperatures approaching 44 degrees Celsius in several regions.
Long wave
For his part, Dr. Ali Qutb, Professor of Climate at Zagazig University and former Deputy Chairman of the Meteorological Authority, explained that the summer usually witnesses severe heat waves of no more than two or three days.
But the current year, according to him, is the continuation of the current wave to more than a continuous week, as the maximum temperatures exceed the 40 ° C in Egypt and most parts of the Arab region.
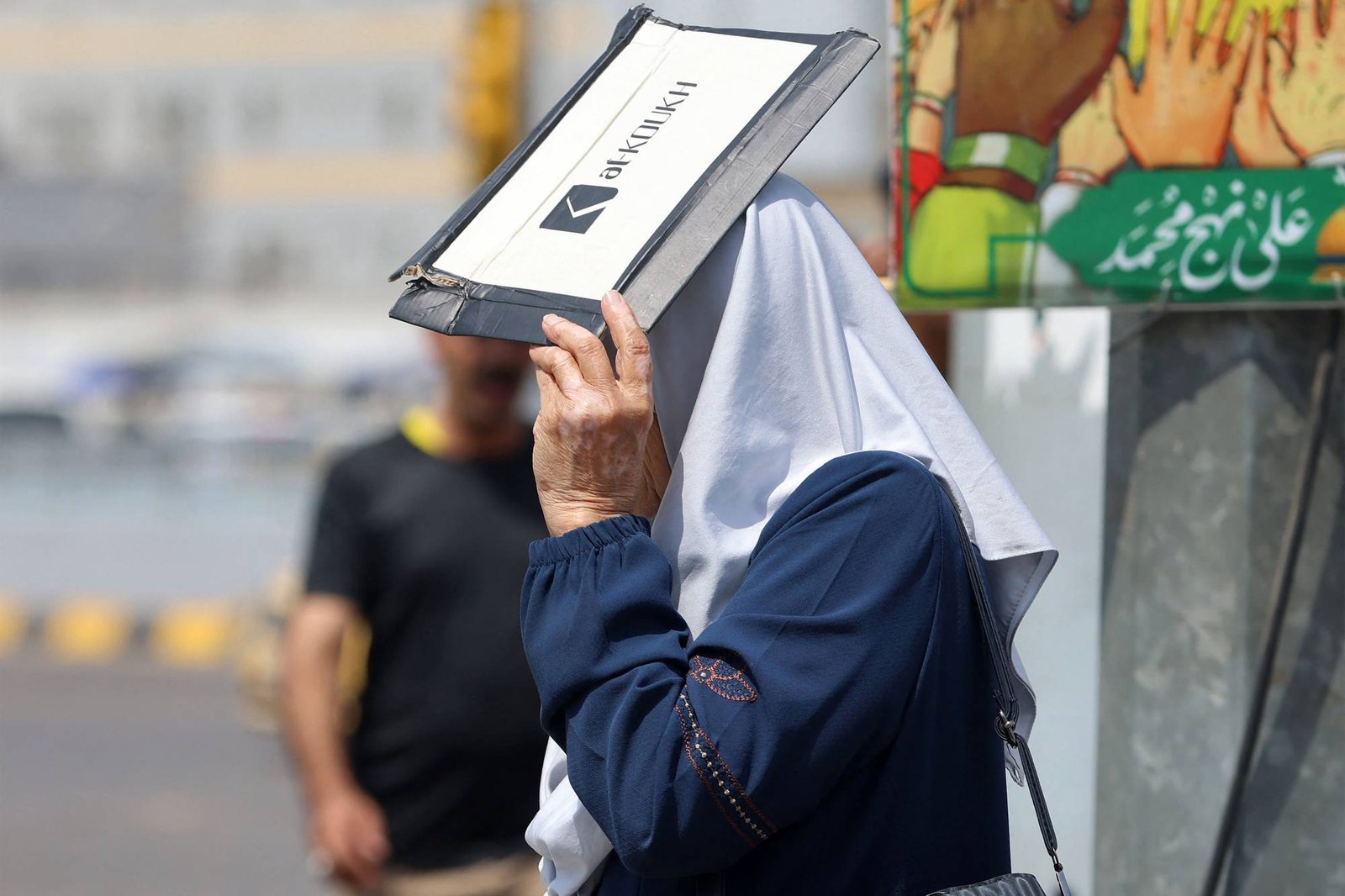
Dr. Ali Qutb said, in an interview with Asharq Al -Awsat, that this long and hot wave affected the Middle East region in general, and coincided with a noticeable increase in humidity rates, which led to an increase in the feeling of heat strongly among citizens.
He indicated that the main reason behind this wave is due to the region’s influence on the seasonal India depression, in conjunction with the presence of an air high in the upper atmosphere, which contributed to the continued high temperatures, indicating that the distribution of air pressure in the upper layers also helped to deepen the effect of the heat.
He added that there is an inverse relationship between wind activity and relative humidity ratios; The higher the movement of the wind, the greater the ability of the air to carry water vapor, which leads to the high humidity rates and thus increases the feeling of the heat of the weather.
For his part, Dr. Mahmoud Shaheen, Director General of Predictions and Early Warning at the Egyptian Meteorological Authority, said that Egypt and the Arab region are currently going through a very hot wave as a result of the deep seasonal season of India, which covers all regions and cities.
He pointed out that what distinguishes this wave from its predecessors is that the high temperatures coincide with a noticeable rise in humidity and water vapor in the air masses, which increases the feeling of citizens with the heat of the weather.

Dr. Mahmoud Shaheen explained to Asharq Al -Awsat that the airbags that raise temperatures are usually somewhat dry, but the currently influential blocs are very wet, as the percentage of small humidity in Egypt is approaching 50 percent.
He pointed out that this increases the heat sensation significantly, compared to the temperatures actually recorded, which are usually measured in the shade. He added that the temperatures differed during the daytime hours in different parts of Egypt, where in some areas it reached between 44 and 45 degrees Celsius.
Does the height continue?
According to specialists at the “Arab Weather” regional center, weather maps show jet currents with late July and early August, allowing the progress of a less hot and more humid air mass towards the eastern Mediterranean.
It is expected that the hot wave in Egypt will be broken during the next few days, with a noticeable decline in temperatures and its return to its usual rates. The effects of this bloc seem to be clearer in the Levant, where the moderate summer atmosphere returns, and the percentage of humidity increases with the activity of marine winds and the emergence of low clouds, which may lead to local rains on the Syrian and Lebanese coasts, according to “Arab Weather”.
It is also expected that the effect of the moderate air mass to Iraq will extend, which contributes to breaking the hot wave severity there, and low temperatures, with the activity of the exciting wind of dust and dust.

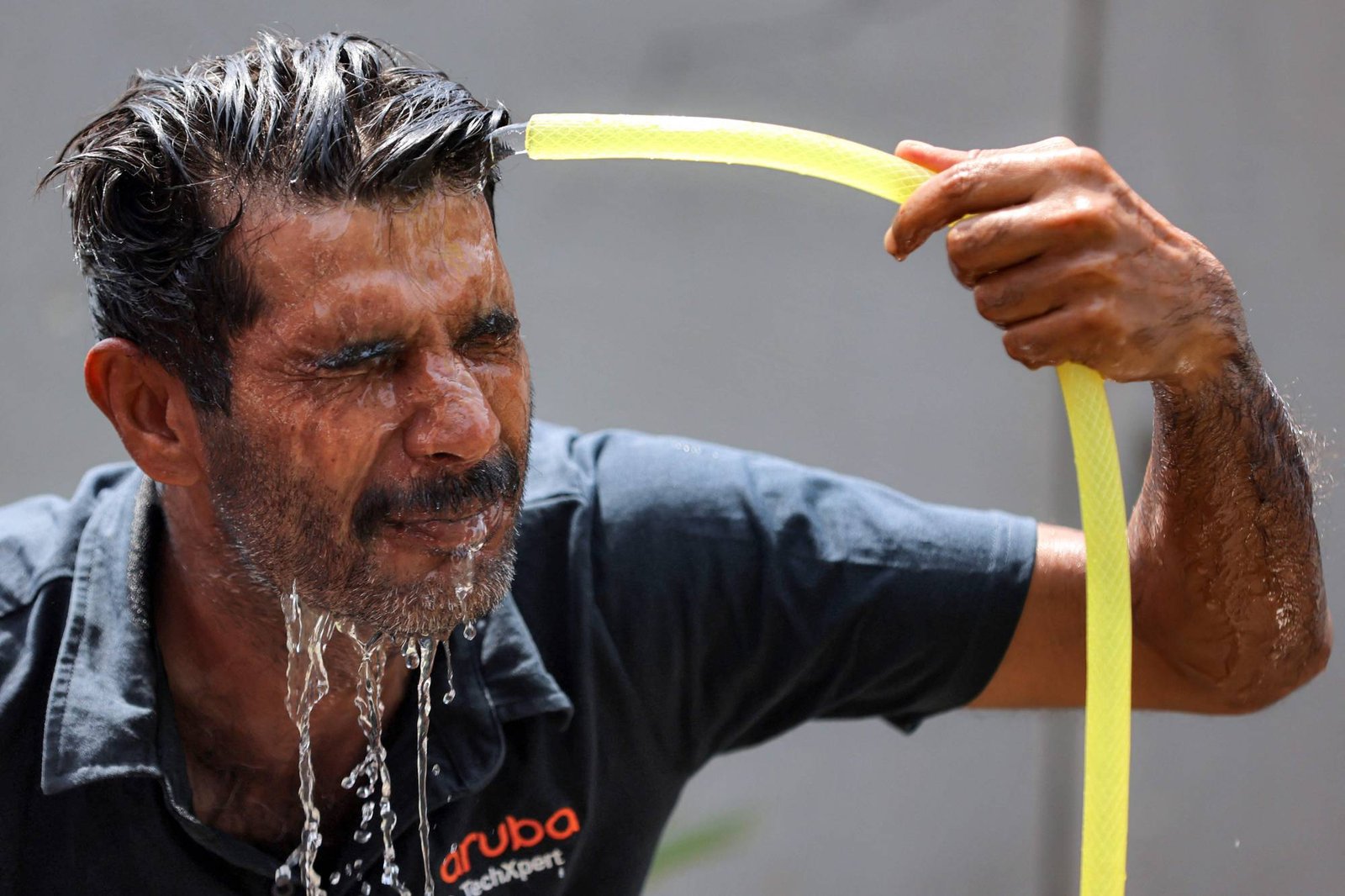
On the possibility of record temperatures in the Arab region, Qutb indicated that there is a possibility to record record or close temperatures in some Arab regions, especially with the continued effect of the seasonal depression of India and the high humidity rates, which increases the feeling of heat.
But he added that this wave, despite its intensity and its unusual length, does not necessarily mean breaking the previous records recorded, as the maximum temperatures exceeded 48 degrees Celsius in some regions of the Middle East, but rather reached more than 50 degrees Celsius in countries such as Kuwait and southern Egypt, but the repetition of such waves during the month of August is very possible, in light of the continuing climate changes and global warming.
While the Director General of Predictions and Early Warning at the General Authority of the Egyptian Meteorology pointed out that climate changes play a prominent role in prolonging the wave period, as the week exceeded in the Middle East and North Africa region, expected to start the wave by refraction in Egypt next Wednesday.
Shaheen added that these changes contributed to increasing the extremism of the heat wave, as high temperatures coincided with a significant increase in humidity rates.
Shaheen expected that the current wave was the most severe during the summer of 2025, suggesting that Egypt will not record higher temperatures during the remainder of the summer, as the next waves will be less severe.
Fort rises
Historically, cities around the world have scored maximum temperatures over the decades, in some of them reaching records that threaten life.
In the “Valley of Death” area of California (United States), the highest temperature in modern history was recorded at 56.7 ° C in 1913, while the surface temperature was about 93.9 degrees Celsius in 1972, according to the BBC.

The Tunisian city of Kebli ranked second globally with a temperature of 55 degrees, which was recorded in 1931, followed by the Iranian city of Ahvaz, which recorded 54 degrees in 2017.
In the list of the most hot cities around the world, the cities of Kuwait and Basra in Iraq emerged at temperatures of 53.9 degrees Celsius, outperforming a city that was raised in Pakistan, which recorded 53.7 degrees Celsius. The Al -Jazeera border crossing in the Emirates also witnessed a heat of 52.1 degrees Celsius, while in the Mexican city of Mexico, 52 degrees Celsius were recorded.
As for the city of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, it recorded the highest temperature in its history at 52 degrees Celsius in June 2010, while the temperature in the Egyptian city of Aswan reached 51 degrees Celsius in July 1918 and 49.6 degrees Celsius in July 2024, which clearly reflects that the Middle East and North Africa region is among the most affected by the world.













0 Comments